HOW DOES IT HELP YOU?
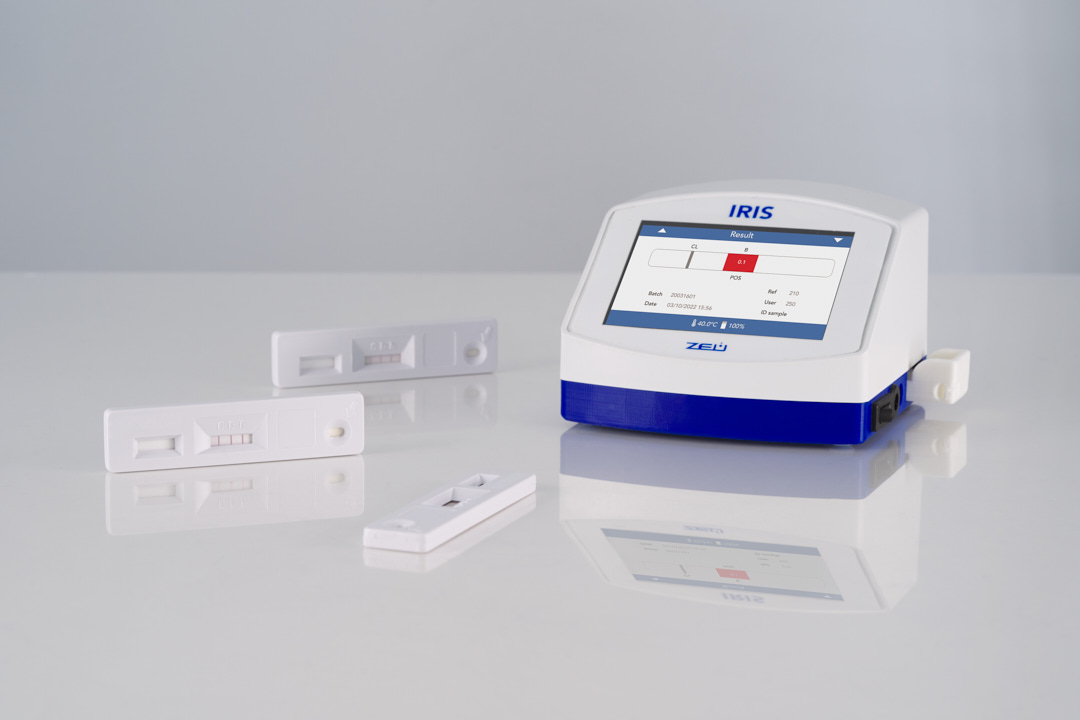
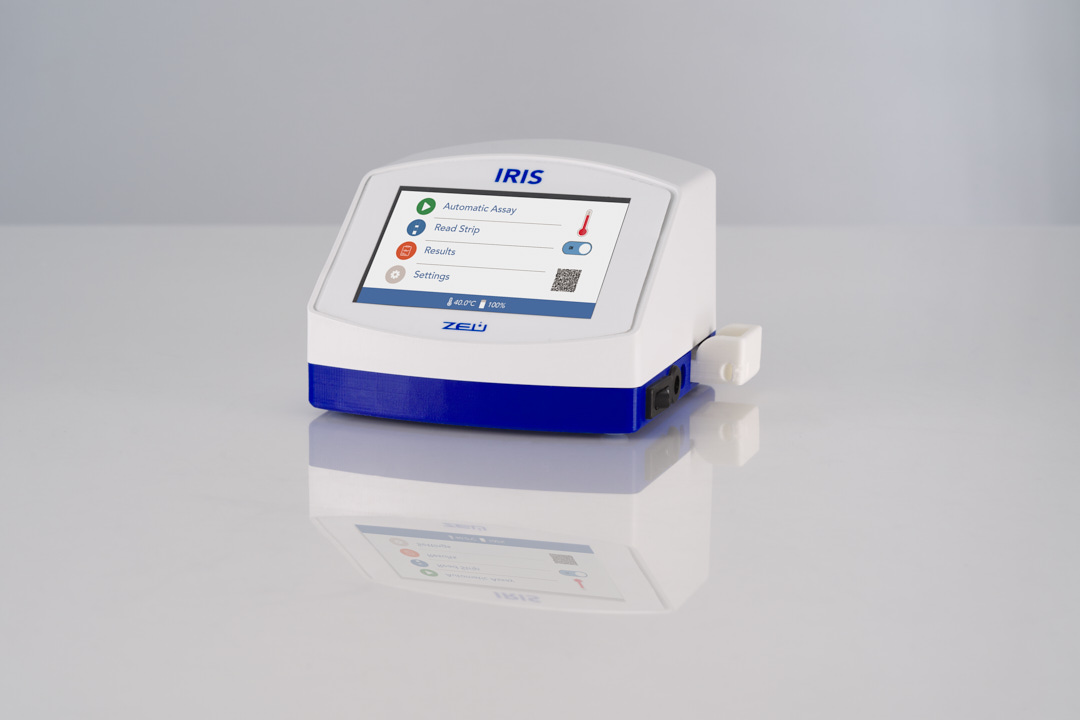
BetaScan helps you to identify if the tank milk is contaminated with beta-lactams during transport or upon arrival at the plant in a simple and fast way. Once the operator sets the automatic test at the reception, or even on the truck, the results will be automatically received in-real time allowing to make quick decisions.
BetaScan analysis at the farm helps avoid industry penalties. Just by adding a drop of milk, you can check the tank in a few minutes before the milk is collected. In addition, you can share the results with the plant personnel to daily guarantee the quality of your milk.